3035 Washington Rd Suite 3, McMurray, PA 15317

Oral cancer is a serious condition that can affect any part of the mouth, including the lips, tongue, cheeks, and throat. Improved survival rates and successful treatment depend on early diagnosis. Understanding the early symptoms of oral cancer can help you seek timely medical attention and potentially save your life. This piece will examine the essential symptoms must be aware of, danger signs, and the significance of regular dental check-ups.
About Oral Cancer
Oral cancer refers to cancers that develop in the tissues of the mouth or throat. It typically begins as a painless lesion or sore that doesn’t heal. Over time, these lesions can grow, leading to more severe symptoms. Squamous cell carcinoma is the most prevalent kind of oral cancer, which arises in the flat cells lining the mouth and throat.
Risk Factors for Oral Cancer
Before delving into the symptoms, it’s essential to comprehend the risk variables connected to mouth cancer. Being aware of these factors can help you assess your risk and take preventive measures.
- Tobacco Use: Smoking cigarettes, cigars, or pipes, as well as using chewing tobacco, significantly increases the risk of oral cancer. The harmful chemicals in tobacco damage the cells in the mouth, leading to mutations and cancer development.
- Alcohol Consumption: Heavy alcohol consumption is another major risk factor. Alcohol irritates the cells in the mouth and makes them more susceptible to cancerous changes. Additionally, when combined with tobacco use, this effect becomes even more pronounced.
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV): Certain strains of HPV, particularly HPV-16, are linked to oropharyngeal cancers, including those in the tonsils, base of the tongue, and back of the throat.
- Sun Exposure: Lip cancer risk is increased by prolonged sun exposure. People who spend a lot of time outdoors without protecting their lips with sunscreen or a hat are at higher risk.
- Age and Gender: Oral cancer is more common in older adults, particularly those over 50, and is more prevalent in men than in women.
- Diet: A diet lacking in fruits and vegetables may make you more susceptible to oral cancer. These foods contain essential vitamins and antioxidants that help protect cells from damage.
Early Signs of Oral Cancer
Identifying the early symptoms of oral cancer is crucial for prompt diagnosis and treatment. The following symptoms are often associated with the initial stages of the disease:
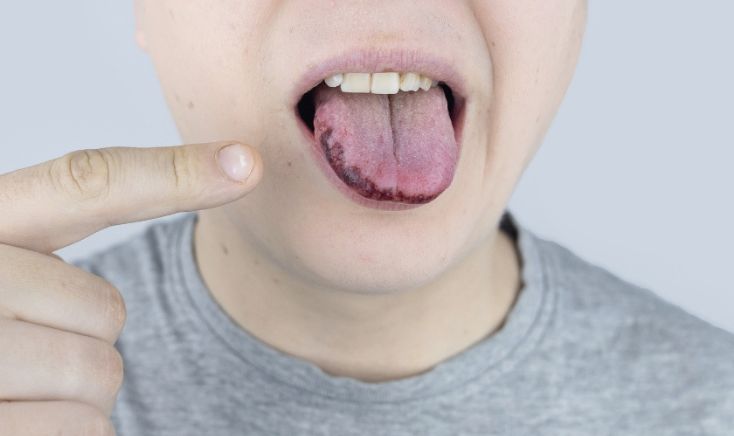
- Persistent Mouth Sores: Among the most prevalent early indications of oral cancer is a sore in the mouth that doesn’t heal within two weeks. These sores can appear anywhere in the oral cavity, including the gums, tongue, and inner cheeks.
- Red or White Patches: Red (erythroplakia) or white (leukoplakia) patches in the mouth can be precancerous lesions. Not all red or white patches are cancerous, but you should have them examined by a medical professional if they persist.
- Lump or Thickening: A lump, thickening, or rough spot in the mouth or throat can indicate the presence of oral cancer. These changes may feel like a bump or a hardened area that doesn’t go away.
- Unexplained Bleeding: Bleeding in the mouth that isn’t associated with injury or dental procedures should be investigated. Oral cancer can cause spontaneous bleeding, particularly if the tumor invades blood vessels.
- Difficulty Swallowing (Dysphagia): Trouble swallowing or the sensation that something is caught in the throat may be an early sign of throat cancer. This symptom is particularly concerning if it persists and is accompanied by pain.
- Numbness or Pain: Unexplained numbness, pain, or tenderness in the face, mouth, or neck can be an early indicator of oral cancer. These symptoms may result from nerve involvement as the tumor grows.
- Voice Changes: Persistent hoarseness, a change in voice, or a persistent sore throat can be symptoms of cancer of the larynx or throat.
- Loose Teeth or Dentures: Oral cancer can affect the gums, leading to loose teeth or ill-fitting dentures. If you observe alterations in the way your teeth mate or discomfort with your dentures, consult a dentist.
- Ear Pain: Chronic ear pain without an ear infection can be related to oral cancer, especially if it occurs on one side and is accompanied by throat discomfort.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Like many cancers, oral cancer can cause unexplained weight loss due to difficulty eating, loss of appetite, or the body’s increased energy expenditure.
Importance of Regular Dental Check-Ups
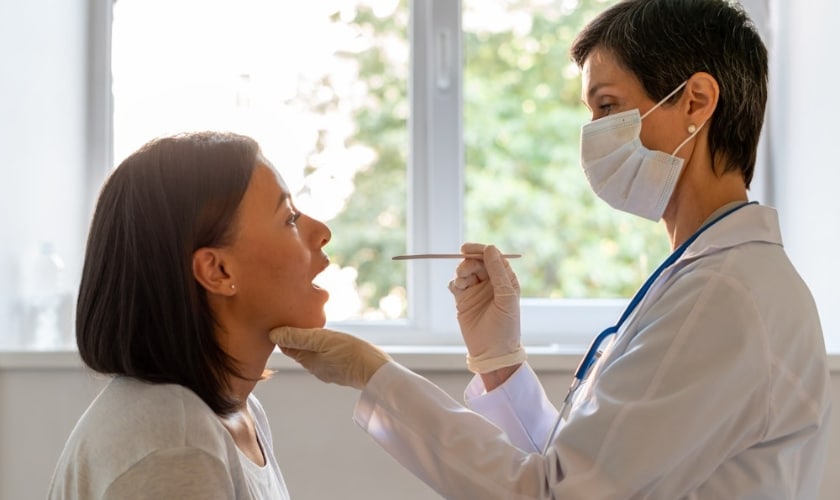
Frequent dental examinations are essential for the early detection of oral cancer. Dentists are educated to identify the telltale indications and manifestations of oral cancer during routine exams. They can identify abnormalities in the mouth and if required, send patients to experts for additional assessment.
During a dental visit, your dentist will perform an oral cancer screening. This involves visually examining your throat and mouth, and palpating your neck and jaw for lumps. Some dentists use special tools like VELscope or brush biopsies. These tools help detect abnormal cells that may not be visible to the naked eye.
What To Do If You Suspect Oral Cancer?
If you notice any of the early symptoms of oral cancer, it’s important to seek medical attention promptly. Your dentist or doctor will likely perform a thorough examination and may order a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis. Prompt identification considerably raises the likelihood of effective therapy and recuperation.
Depending on the stage and kind of oral cancer, treatment options of the tumor. Common treatments include surgery to remove the tumor, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. In some cases, doctors may use targeted therapy or immunotherapy.
Overall, Oral cancer is a serious condition that requires early detection for effective treatment. By being aware of the risk factors and early symptoms, you can take proactive steps to protect your oral health. Regular dental check-ups are essential for detecting oral cancer early. Early detection is crucial because it allows for more effective treatment. By catching the disease in its initial stages, patients have a better chance of successful intervention.
If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned in this article, don’t hesitate to contact your dentist or healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation.
Taking charge of your oral health and being vigilant about changes in your mouth can make all the difference in preventing and treating oral cancer. Stay informed, stay proactive, and prioritize your dental health to reduce your risk of this potentially life-threatening disease.